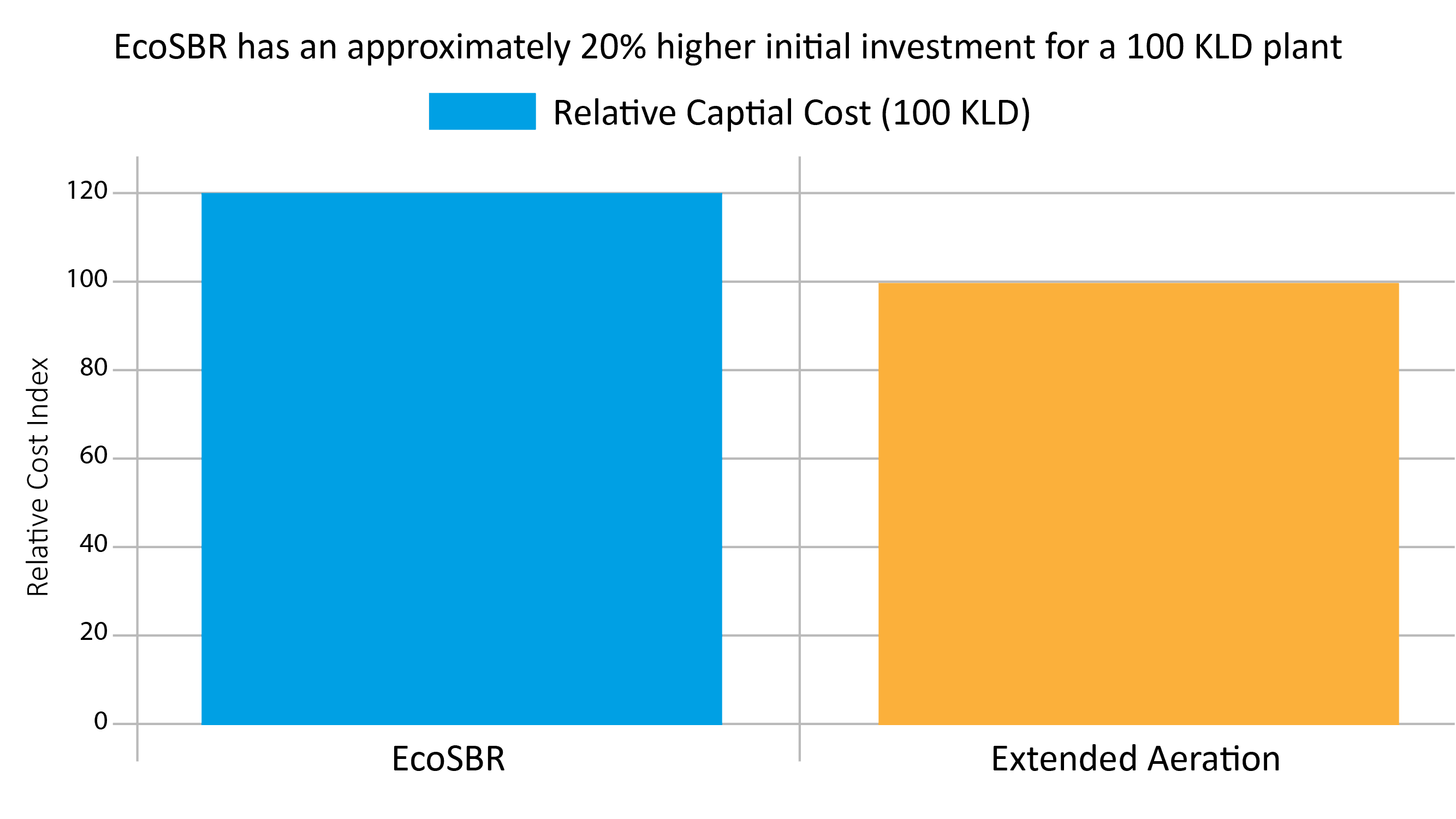Comparison of: EcoSBR vs. Extended Aeration
Understanding the modern advancements in EcoSBR compared to the traditional Extended Aeration process for wastewater treatment.
Process Overview
Key Comparative Features
> Capital Costs (100 KLD Plant)
For a 100 KLD plant, EcoSBR's capital cost is approximately 20% higher than a typical Extended Aeration process, reflecting its advanced features and integrated capabilities.
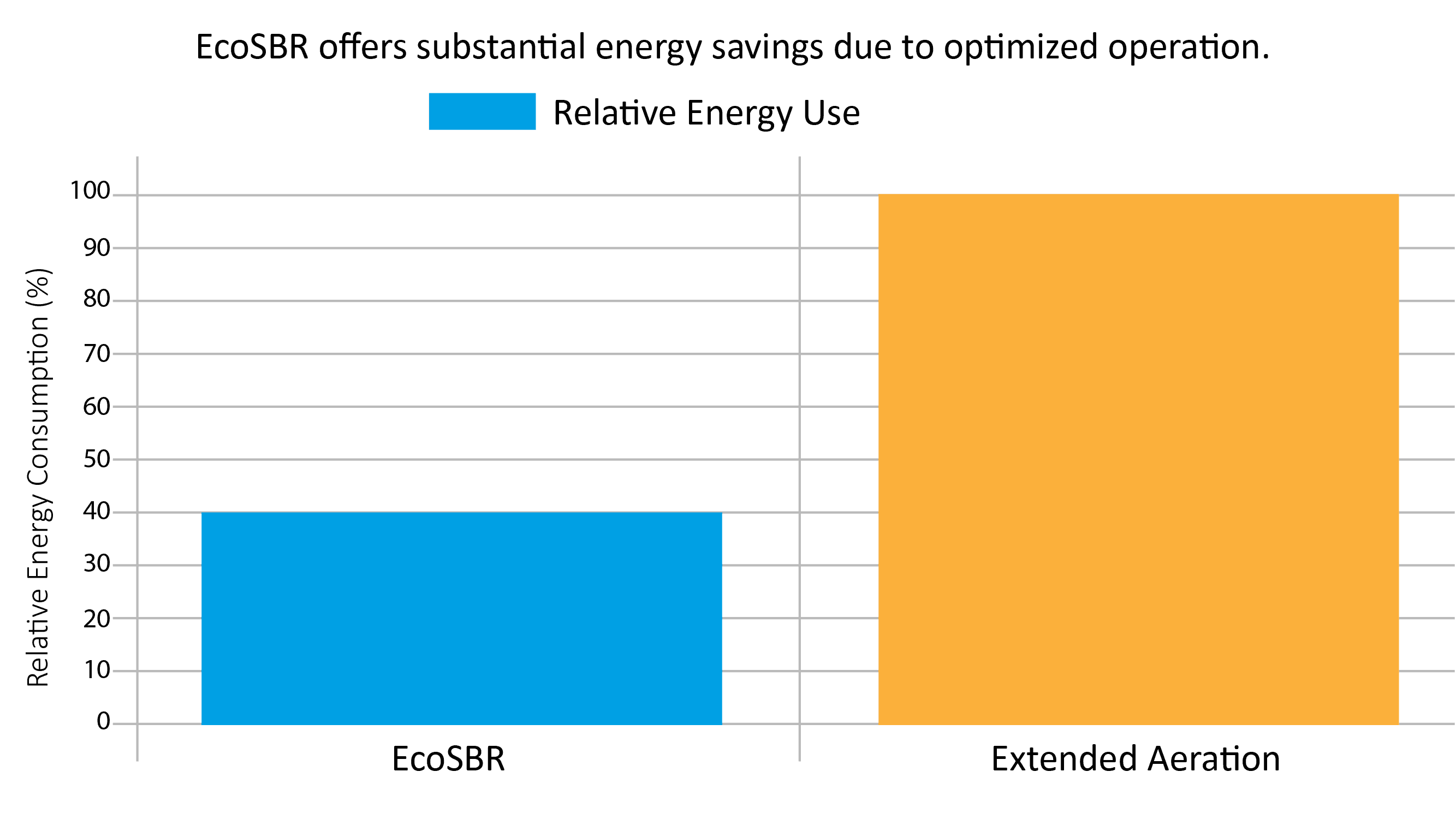
> Energy Consumption
EcoSBR's optimized aeration cycles and air-lift technology lead to significantly lower energy use compared to continuous aeration in Extended Aeration.
> Operational Simplicity & Skill Needs
EcoSBR's high automation minimizes operator intervention, while Extended Aeration requires more routine monitoring and manual adjustments.
> Nutrient Removal Capabilities
EcoSBR is inherently designed for advanced nutrient removal within a single basin, while Extended Aeration may require additional units for comprehensive nitrogen and phosphorus removal.
> Physical Footprint
EcoSBR's single-basin design often offers a more practical and simpler solution than the combined aeration and separate clarifier of Extended Aeration.
> Sludge Management
EcoSBR's optimized conditions lead to lower sludge volume and easier management compared to Extended Aeration.
With EcoSBR there is lower sludge production, easier to dewater, long storage capacity. While in E
Extended Aeration
Reduced sludge vs. conventional, but higher than EcoSBR and may require more frequent handling.
Key Advantages of EcoSBR
> Superior Energy Efficiency
EcoSBR's intermittent aeration and intelligent load-based operation (EcoSave mode) significantly reduce power consumption compared to the continuous, often less optimized, aeration in Extended Aeration. It can operate on very low power, even for minutes per day during low flow periods.
> Automated & Low-Skill Operation
Equipped with advanced controllers and IoT capabilities, EcoSBR systems are fully automatic, drastically reducing the need for skilled operators and minimizing human errors, a stark contrast to the more hands-on operation of Extended Aeration.
> Enhanced Nutrient Removal
EcoSBR's ability to achieve comprehensive biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal in a single basin is a significant advantage over Extended Aeration, which often requires additional stages or chemical dosing for comparable nutrient reduction.
> Mechanical Simplicity & Reliability
The absence of in-tank mechanical moving parts and reliance on clog-resistant air-lift pumps in EcoSBR drastically reduces maintenance and downtime, offering higher reliability than systems with submerged mechanical components typical of Extended Aeration.
> Lower Overall Costs
Combining lower energy consumption, reduced maintenance, and minimal operator dependency, EcoSBR generally offers a lower total cost of ownership (CAPEX + OPEX) compared to Extended Aeration over the plant's lifespan.
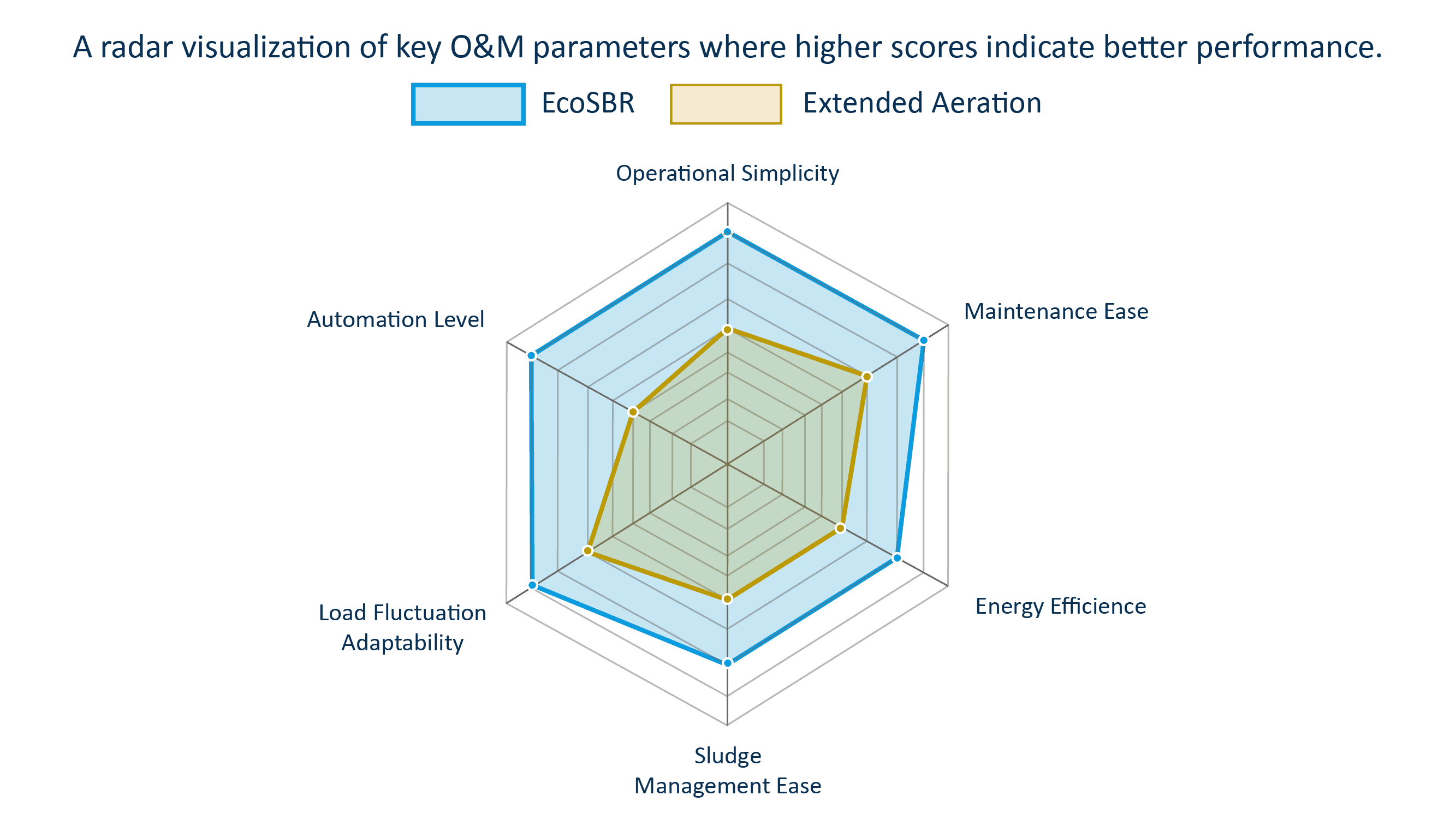
Key Operational & Maintenance Metrics
EcoSBR generally performs better in areas related to automation, lower skill requirements, and simplified maintenance due to fewer in-tank mechanical parts. Extended Aeration offers good overall reliability but typically requires more manual oversight and has higher energy needs due to continuous operation.
Decision making
While Extended Aeration remains a viable and robust option for many applications, EcoSBR represents a significant leap forward in wastewater treatment technology. Its emphasis on automation, energy efficiency, and advanced nutrient removal within a simplified operational framework positions it as a highly attractive choice for modern wastewater treatment needs.
Consider EcoSBR for projects where long-term operational cost savings, minimal human intervention, and high-quality effluent with comprehensive nutrient removal are key priorities.